Vol.01, Issue-01, July 2024
Authors
- Dr. Manish Singh Tomar, MD (Ay), MBA, CCPT, PGDYM, PGDPC
Assistant Professor, SRS Ayurvedic Medical College & Hospital, Agra, Uttar Pradesh, India - Dr. Shashank Malik, BAMS
Consultant Physician (Ayurveda), Ayurhridayam Clinic & Panchakarma Center, Noida, Uttar Pradesh, India
Abstract
This clinical study evaluates the efficacy of X Compound DS capsules in treating erectile dysfunction (ED) and premature ejaculation (PME). X Compound DS capsules, when administered with Chandraprabha Vati, were found to significantly improve the frequency, quality, and sustainability of erections, as well as increase the duration of intercourse by delaying semen discharge. Patients reported enhanced sexual desire and an increased readiness to initiate sexual activity. The study suggests that X Compound DS capsules offer a safe, economical, and effective treatment option for ED and PME.
Keywords
Erectile Dysfunction, Premature Ejaculation, X Compound DS, Chandraprabha Vati, Ayurvedic Medicine, Sexual Health
Introduction
Erectile dysfunction (ED) and premature ejaculation (PME) are common sexual disorders affecting men globally, with significant impacts on quality of life and interpersonal relationships. ED is characterized by the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for sexual activity, while PME involves ejaculation that occurs sooner than desired, with minimal stimulation. Conventional treatments include psychotherapeutic approaches, pharmacotherapy, and, in severe cases, surgical interventions. This study focuses on the efficacy of X Compound DS capsules, in combination with Chandraprabha Vati, for the treatment of these conditions.
Materials and Methods
This open clinical trial was conducted at Ayurhridayam Clinic & Panchakarma Center, Noida, Uttar Pradesh, India. Thirty men aged 19-59 years, suffering from both ED and PME, were selected based on specific inclusion and exclusion criteria. Patients were administered X Compound DS capsules and Chandraprabha Vati once daily after dinner for four weeks. Sexual functioning was evaluated using the International Index of Erectile Functioning (IIEF) at baseline, two weeks, and four weeks.
Inclusion Criteria
- Men aged 18 years or older
- Experiencing ED and PME for more than three months
- At least a 50% failure rate to maintain an erection over four attempts in a treatment-free baseline period
Exclusion Criteria
- Anatomical abnormalities of the penis
- History of radical prostatectomy, spinal cord injury, unstable angina, or myocardial infarction
- Poorly controlled diabetes mellitus with complications
- Use of hormonal treatments or psychoactive drugs
Results and Discussion
Erectile Function Improvement
Significant improvements in erectile function were observed after two and four weeks of treatment. Patients reported better ability to penetrate, maintain erections, and increased confidence in sustaining erections throughout intercourse.
Satisfaction from Sexual Activity
Therapy with X Compound DS and Chandraprabha Vati led to higher satisfaction levels from sexual intercourse. Patients reported greater willingness to initiate sexual activity and higher overall satisfaction from intercourse.
Orgasmic Function and Sexual Desire
The treatment also positively influenced orgasmic function, increasing the frequency of orgasms and ejaculations. Sexual desire improved significantly, with patients reporting enhanced levels of sexual interest and arousal after four weeks.
Overall Satisfaction
Patients expressed overall satisfaction with the treatment, with a majority reporting improved sexual life and better relationships with their partners.
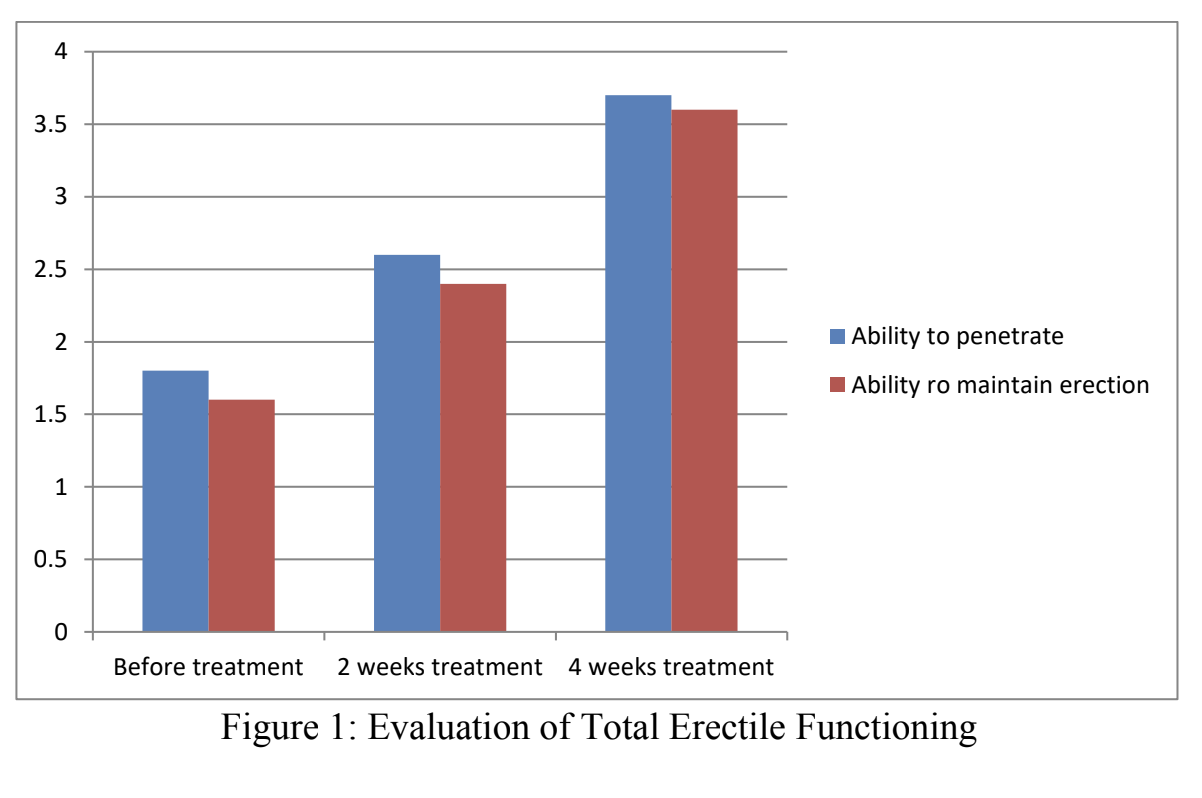
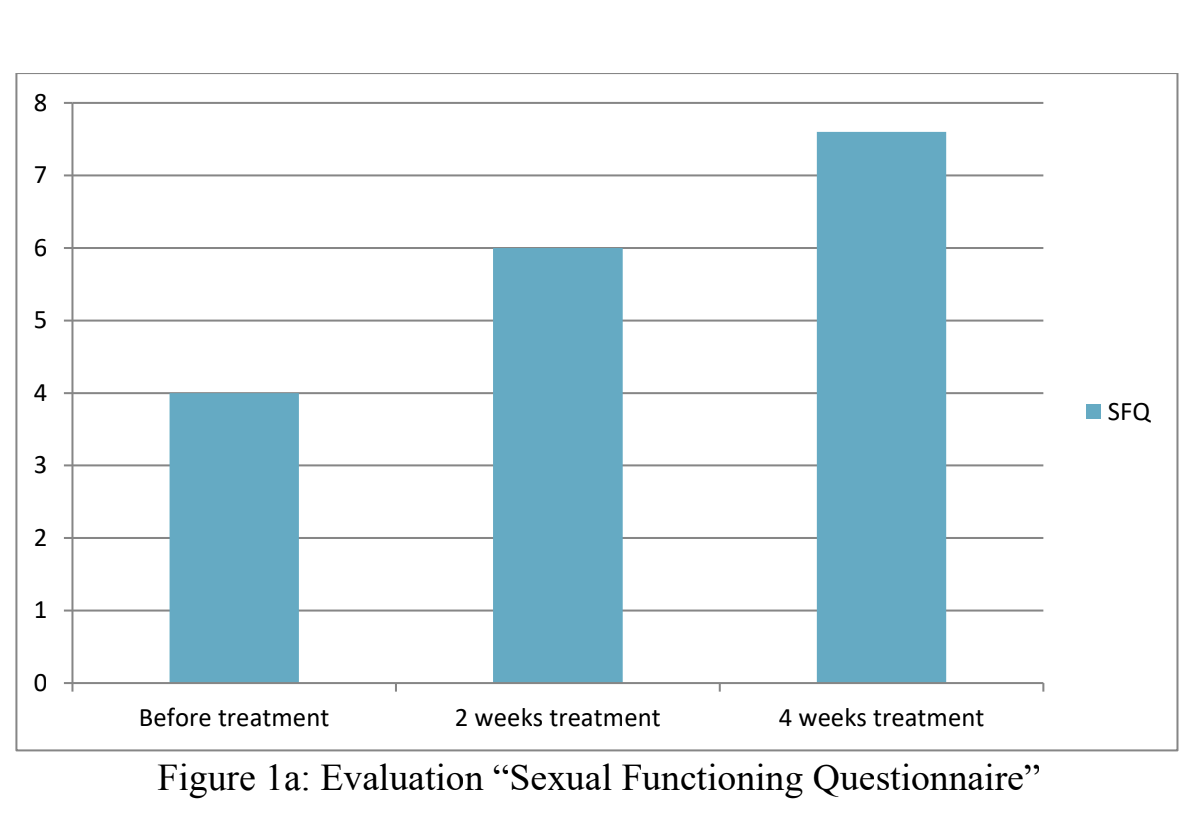
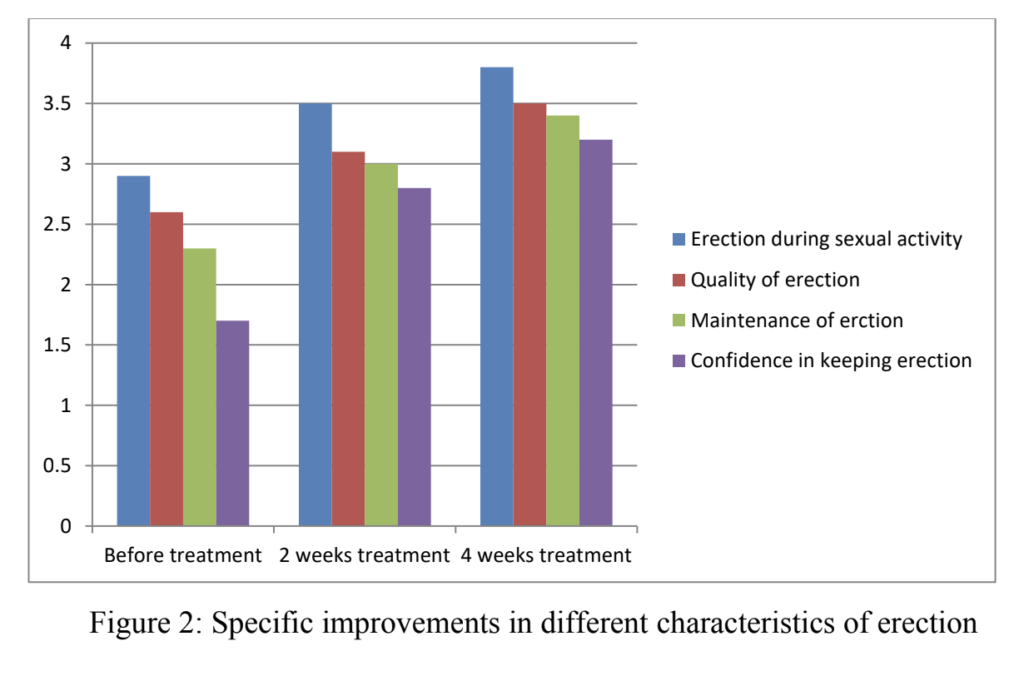
Conclusion
The clinical trial demonstrated that X Compound DS capsules, in combination with Chandraprabha Vati, are effective in treating erectile dysfunction and premature ejaculation. The therapy enhances sexual desire, improves erection quality, and increases overall satisfaction with sexual activity, making it a viable and economical option for patients with these conditions.
References
- National Institute of Health (NIH) Consensus Conference. Impotence. NIH Consensus Development Panel on Impotence. JAMA 1993; 270: 83-90.
- Feldman, H.A., Goldstein, I., Hatzichristou, D.G., Krane, R.J., McKinlay, J.B. Impotence and its medical and psychosocial correlates: Results of the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. Journal of Urology 1994; 151: 54-61.
- Ayata, I.L., McKinlay, J.B., Krane, R.J. The likely worldwide increase in erectile dysfunction between 1995 and 2025 and some possible policy consequences. BJU Int. 1999; 84: 50-56.
